Manage Azure Storage
About this guide
Scenario
Your organization is currently storing data in on-premises data stores. Most of these files are not accessed frequently. You would like to minimize the cost of storage by placing infrequently accessed files in lower-priced storage tiers. You also plan to explore different protection mechanisms that Azure Storage offers, including network access, authentication, authorization, and replication. Finally, you want to determine to what extent Azure Files is suitable for hosting your on-premises file shares.
Job Skills
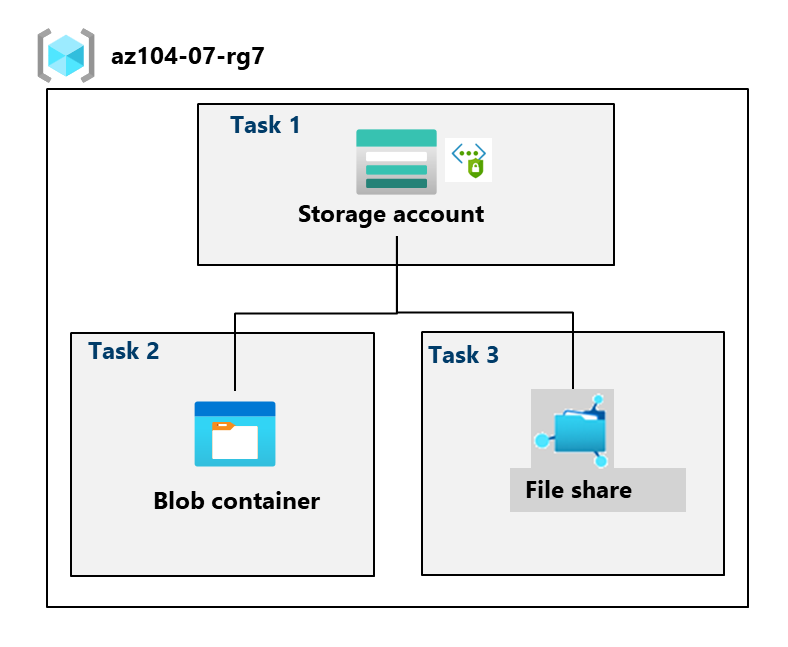
Task 1: Create and configure a storage account
Task 2: Create and configure secure blob storage
Task 3: Create and configure Azure file storage
As organizations around the world migrate solutions to the cloud, the ability to implement, manage, and monitor cloud-based solutions is highly valued in numerous industries.
Architecture Diagram
Key Takeaways:
- An Azure storage account contains all your Azure Storage data objects: blobs, files, queues, and tables. The storage account provides a unique namespace for your Azure Storage data that is accessible from anywhere in the world over HTTP or HTTPS.
- Azure storage provides several redundancy models including Locally redundant storage (LRS), Zone-redundant storage (ZRS), and Geo-redundant storage (GRS).
- Azure blob storage allows you to store large amounts of unstructured data on Microsoft’s data storage platform. Blob stands for Binary Large Object, which includes objects such as images and multimedia files.
- Azure file Storage provides shared storage for structured data. The data can be organized in folders.
- Immutable storage provides the capability to store data in a write once, read many (WORM) state. Immutable storage policies can be time-based or legal-hold.
Career Connections
With the increasing demand for expertise in cloud-based administration, professionals with the skills from this series can pursue job prospects in roles such as Azure Administrator, Cloud Engineer, Systems Administrator (Cloud Focus), DevOps Engineer, and Cloud Support Engineer.
As of 2025, average cloud-related salaries in the United States range from $68,215 for entry-level Azure Administrators to $130,000 for mid-career DevOps Engineers, with Cloud Engineers, Systems Administrators, and Cloud Support Engineers earning competitive pay based on experience and role demands. Please note that these figures are approximate, derived from online sources, and can vary based on factors such as location, industry, and company size.